What is Placement in Money Laundering?
Money laundering is a process of cleansing illegal funds or an effort to conceal the origin of the criminal proceeds. The money layering process consists of three stages – placement, layering, and integration. Placement is the first step where the criminals introduce illegally acquired money into the legal system. It is the process to make unlawful money appear legal by placing it into legalized financial institutions. Let’s discuss more on what placement is in money laundering and how businesses can prevent misuse of their organization by criminals from being used as a conduit to enter the financial system.
What is placement in money laundering?
Placement means placing or introducing money into the legal system using different methods. Criminals get unlawful money from various criminal activities such as corruption, trafficking, extortion, etc., and run this money through the legal system, consisting of banks and financial institutions. After the money is placed into the legal system, it is layered with multiple transactions from one bank account to another in the same institution or several financial intuitions in different bank accounts and offshore accounts.

This activity, known as layering, creates layers of dummy transactions and distances the original transaction and funding source. Criminals later withdraw the money, which by this time, is passed through a series of transactions, making it difficult for the authorities to determine its source.
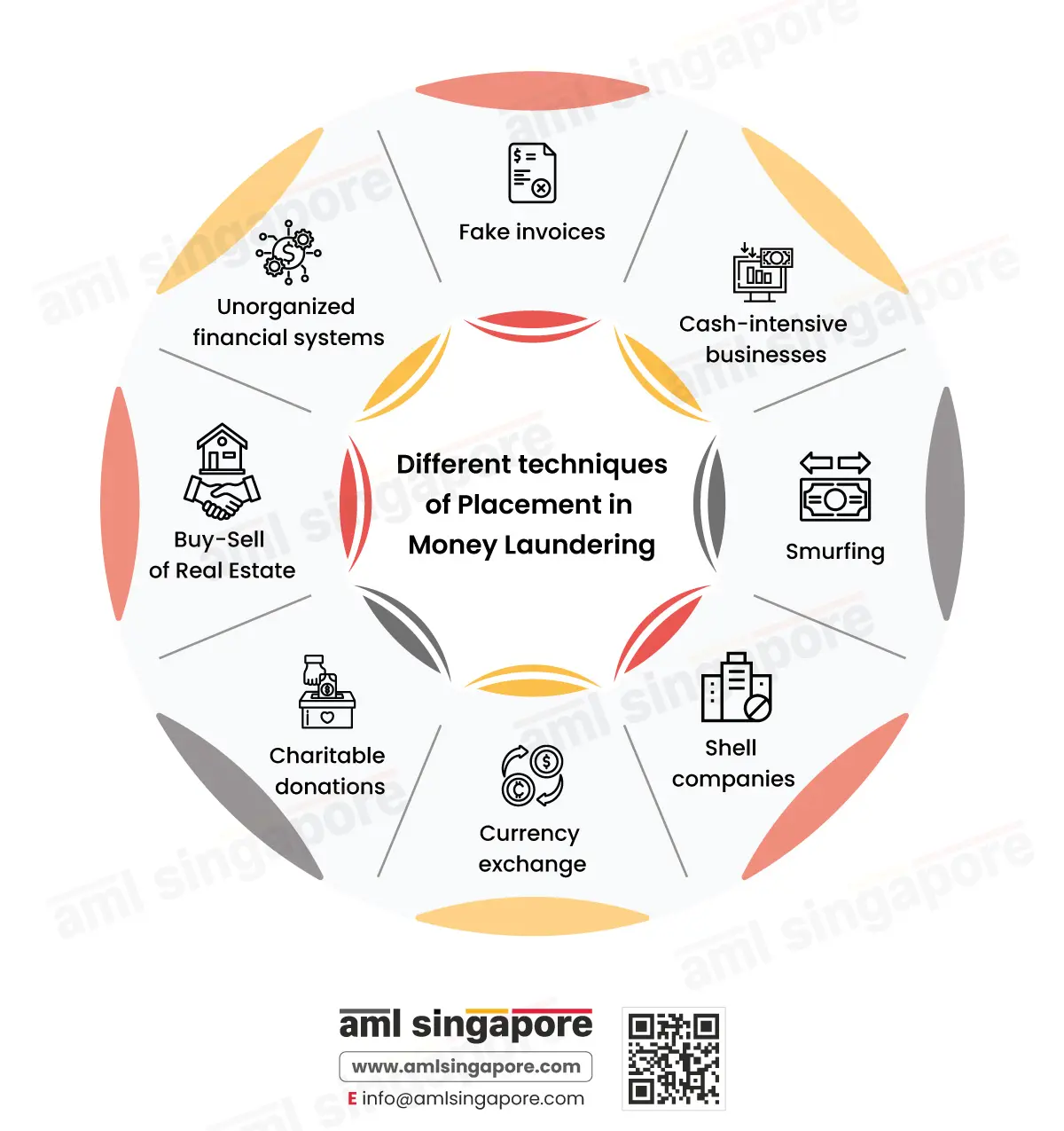
Different Methods of Placement in Money Laundering
Money launderers use different methods to move their illegally-acquired money into the legitimate economy.
Fake invoices:
One of the most used methods of making illegal money appears lawful. Fake invoices are generated for goods not purchased from the legal businesses the fraudsters might own. Trade manipulation in the form of inflated and deflated invoices is also the trick criminals use to move illegal money and blend it with the legitimate economy. This method of placing funds into the financial system using various trade techniques is known as Trade-based Money Laundering, wherein bogus documentation is generated to move the funds locally or internationally.
Cash-intensive businesses:
Often, criminals spend illegally acquired money in businesses where cash is prominently used, such as casinos, bars, etc
Smurfing:
The method involves breaking down a large amount of illegal cash into small amounts falling just within the threshold permissible limit from an AML perspective. It is bound to raise suspicions as multiple transactions within the money deposit threshold indicate money laundering. It is one of the most common methods criminals use for laundering money in small amounts. They make micro-transactions several times that go unnoticed, and the money is transferred into foreign bank accounts and then withdrawn in the foreign country.
Shell companies:
Criminals often set up shell companies to deposit illegal money through transactions in the name of these companies. The transfer appears legitimate with the company’s name but is actually a method to conceal and move illicit money into the systems. Further, shell companies also aid the laundering process by creating layers of multiple transactions and eliminating the audit trail to hide the illegal source of the funds.
Currency exchange:
Money exchange houses convert significant cash into another currency and move quickly across the border.
Charitable donations:
A large sum of illegally obtained cash is given as donations to charitable or non-profit organizations, which offers a tax benefit to the donor and is sometimes used to fund terrorist activities.
Buy-Sell of Real Estate:
Money launderers invest illegal criminal proceeds in real estate properties through direct cash deposits. An immediate sale of the property further exploits this to show the illegal funds as proceeds realized from the sale of the property.
Unorganized financial systems:
Unorganized, unregulated financial networks such as the Hawala system are used to conceal illicit funds and transfer them across borders.
Why should businesses combat placement?
Placement is the first step in the complex money laundering process. If thwarted at this stage, it can prevent the criminals from entering the legitimate economy and exploiting it to conclude the laundering process. Let’s discuss the top reasons why placement activity must be prevented proactively.
Prevention of funding criminal and terrorist activities:
The money that goes unaccounted for is used for financing various criminal activities such as bribery, corruption, extortion, smuggling, trafficking, and kidnapping and is even used for funding terrorism and the supply of weapons to carry out terrorist activities.
Threat to the financial system:
Placement causes considerable danger to the country and can destabilize the legal and financial system with the influx of large sums of illegal money into the economy. It increases corruption, bribery, and ownership of assets and projects by transferring them into the hands of criminals.
Reputational damage:
Money laundering causes irreversible damage to financial institutions. When instances of money laundering come into the public domain, they break the customers’ trust and make it difficult for the financial institutions to restore faith in them. It leads to monetary losses as customers do not trust the institution anymore. Therefore regulatory compliance becomes an absolute necessity.
Legal consequences of not following the AML Laws
Assisting or aiding financial criminals to launder illegal funds through your business or AML non-compliance about failure to identify the ML/FT red flags is a criminal offense under AML regulations. Further, suppose a business is found guilty of acquiring, possessing, using, hiding, or transferring property believed to be illegal money, and there are reasonable grounds to identify the facts around funds being criminal proceeds. In that case, hefty penalties are imposed upon the business organizations.
Thus, the regulated organization in Singapore must understand the intricacies of the placement stage of money laundering and make all the efforts to identify such attempts and apply robust mitigation measures to prevent criminal funds from entering the country’s financial system.
How can AML Singapore assist you in fighting money laundering crime?
Placement in money laundering is the first step in introducing unlawful money into the legal system. Criminals use different methods to ‘place’ money into the legal system and withdraw it to fund many criminal activities and terrorism. Businesses should be aware of the red flags and immediately thwart placement activities of introducing illegal cash into the organizations. They must apply strong AML controls, including identifying the customer and performing adequate Customer Due Diligence measures. When dealing with corporate customers, identify the UBOs – Ultimate Beneficial Owners. They should abide by the AML laws or else pay a penalty. They can take the help of experts who have the knowledge and experience to implement the AML laws and prevent criminals from misusing their organization for money laundering.
AML Singapore is one of the leading AML consultants in Singapore, offering a wide range of services that help businesses identify the ML/FT risk indicators and fight these financial crimes. We help clients by creating and maintaining a robust AML framework (internal policies, procedures, and controls – IPPC), designing comprehensive customer onboarding measures, training the team to implement the AML program effectively, etc.
Let’s fight the money laundering vice and safeguard our business and economy!

About the Author
Jyoti Maheshwari
CAMS, ACA
Jyoti has over 7 years of hands-on experience in regulatory compliance, policymaking, risk management, technology consultancy, and implementation. She holds vast experience with Anti-Money Laundering rules and regulations and helps companies deploy adequate mitigation measures and comply with legal requirements. Jyoti has been instrumental in optimizing business processes, documenting business requirements, preparing FRD, BRD, and SRS, and implementing IT solutions.